Introduction
Butane is a highly versatile hydrocarbon gas used in a variety of industrial, commercial, and household applications. It is primarily used as a fuel, as well as a key component in the production of other chemicals, including synthetic rubber, plastics, and synthetic fuels. The Butane Manufacturing Plant Project Report provides a comprehensive overview of setting up a manufacturing facility dedicated to the production of butane. This report includes an analysis of market demand, production processes, raw material sourcing, technology adoption, financial considerations, and regulatory compliance for a successful butane manufacturing operation.
With the rising demand for clean and efficient energy sources, butane has found its place in multiple industries, ranging from energy and automotive to pharmaceuticals and chemicals. Establishing a butane manufacturing plant offers a lucrative business opportunity, especially with the increasing global consumption of liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) and the growing demand for butane as a fuel alternative. This article aims to help investors and entrepreneurs understand the essential components of setting up a butane manufacturing plant, providing insights into both technical and financial aspects.
Understanding Butane and Its Applications
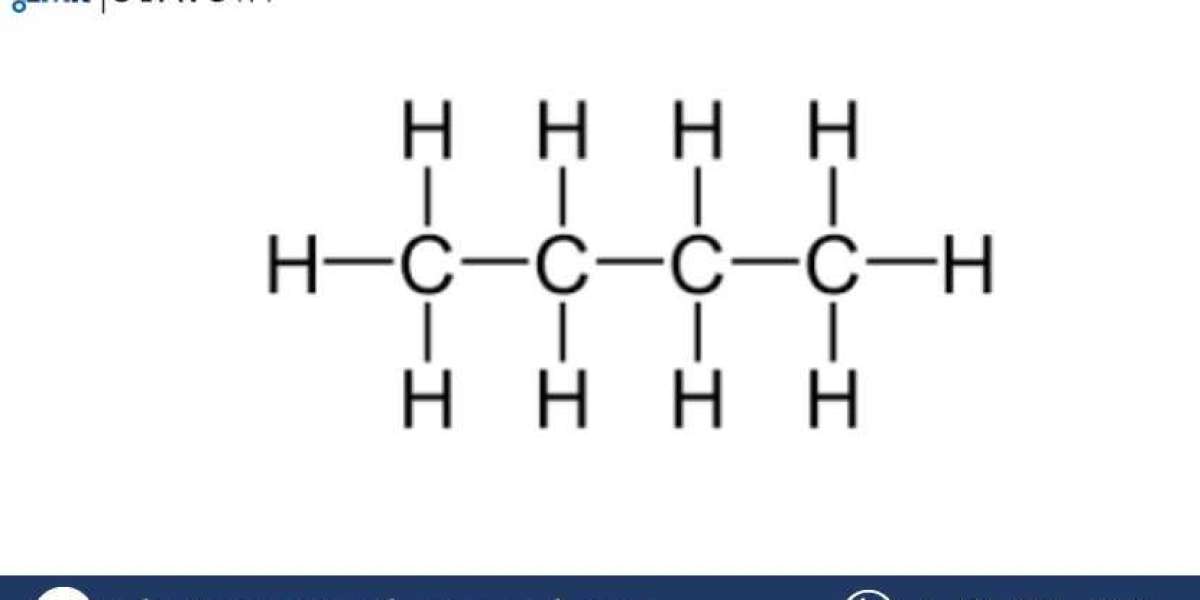
Butane is an aliphatic hydrocarbon with the chemical formula C4H10, and it is a member of the alkane family. It exists as a gas at room temperature but can be easily liquefied under pressure, which makes it convenient for storage and transportation. Butane is primarily derived from natural gas and crude oil processing. It can also be produced through catalytic cracking in petroleum refineries.
Key applications of butane include:
Fuel Source: Butane is widely used as a fuel in residential heating, cooking, and for portable stoves. It is a key component of liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), which is used for cooking and heating in homes and industries.
Automotive Industry: Butane is used as a fuel in certain types of vehicles, particularly in LPG-powered cars. It is also used in the formulation of aerosol propellants.
Chemicals Manufacturing: Butane serves as a key feedstock in the production of chemicals such as isobutane, which is used to produce synthetic rubber, plastics, and various petrochemicals.
Petrochemical Industry: Butane is used in the production of isobutene and other chemicals that are used to manufacture high-demand products like polypropylene, a key material in the plastic industry.
Refrigerants: Butane is also used as a refrigerant, especially in the production of refrigerants like R-600A, which is utilized in refrigeration and air conditioning systems.
Aerosol Propellants: Butane is used as a propellant in aerosol cans for products such as sprays and perfumes. It allows for even distribution of the product in a controlled manner.
Pharmaceutical Industry: Butane is used as a solvent in pharmaceutical applications, particularly in the production of specific drugs and preparations.
Butane’s versatility and wide range of applications make it a critical component of several industries. The global demand for butane is steadily increasing, particularly due to its use in clean fuel applications and its role in the production of valuable chemicals.
Get a Free Sample Report with Table of Contents@
Market Demand and Scope
The global market for butane has been growing, driven by the following factors:
Growth in Energy Demand: The demand for alternative fuels, including LPG, is rising globally, especially in emerging markets. As more countries shift towards cleaner sources of energy, the demand for butane as a fuel component is expected to rise.
Urbanization and Industrial Growth: As industries and urban centers continue to grow, the demand for energy sources like LPG, which contains butane, is increasing. Butane's affordability and ease of use make it an attractive choice for heating and cooking purposes.
Automotive Industry Shift: The global automotive industry is gradually adopting LPG-powered vehicles, increasing the demand for butane as a fuel. Many governments are promoting the use of LPG to reduce air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions, which is further driving market demand.
Petrochemical Industry Expansion: The growing production of plastics, synthetic rubbers, and chemicals is expected to boost the demand for butane in the petrochemical industry. As the demand for products like polypropylene and synthetic rubber increases, so does the need for butane as a raw material.
Sustainability Initiatives: Increasing concerns over climate change and environmental sustainability have led to the adoption of alternative, cleaner fuels. Butane, as part of the LPG family, is a more environmentally friendly option compared to other fossil fuels such as coal and oil.
Global Distribution and Transportation: The global trade and transportation of liquefied petroleum gas, including butane, have become more efficient with advancements in infrastructure and technology. As distribution networks grow, the market for butane is expected to expand.
Given these drivers, the global butane market presents substantial opportunities for investors. As demand rises in both the energy and chemical sectors, setting up a manufacturing plant for butane can offer lucrative returns, especially in regions with growing energy needs.
Project Overview and Objectives
The primary objective of the Butane Manufacturing Plant Project is to establish a high-capacity, efficient, and safe facility capable of producing high-quality butane. The plant will focus on meeting the increasing demand for butane in multiple industries, including energy, chemicals, automotive, and pharmaceuticals. Key goals of the project include:
- High-Quality Production: The plant will produce high-purity butane that meets industry standards and satisfies the requirements of end-users in various sectors.
- Efficiency and Cost Optimization: The plant will utilize state-of-the-art technology and production processes to maximize operational efficiency, minimize energy consumption, and reduce production costs.
- Environmental Sustainability: The project will focus on minimizing environmental impact by implementing sustainable practices such as waste management, emissions control, and energy conservation.
- Market Expansion: The plant will produce butane in various forms and packaging, catering to both domestic and international markets.
- Economic Contribution: The establishment of the plant will create jobs, stimulate local economies, and contribute to the growth of the energy and chemical industries.
Technological Process of Butane Production
Butane is primarily produced through two main processes: natural gas processing and crude oil refining. Below is an overview of the key stages involved in butane production:
Natural Gas Processing: Butane is extracted from natural gas during the processing of raw natural gas. The process typically involves separating the various components of natural gas, including methane, ethane, propane, butane, and others. The extracted butane is then purified and stored for further use.
Crude Oil Refining: Butane is also produced during the refining of crude oil, specifically through the distillation process. During the refining process, crude oil is heated, and the various components are separated based on their boiling points. Butane is typically separated during the distillation of light hydrocarbons and is then further treated and refined.
Isomerization and Cracking: In some cases, butane can be produced through isomerization or catalytic cracking. Isomerization converts straight-chain butane into its more useful branched isomer, isobutane, which is a key raw material in the production of high-octane fuels and chemicals.
Purification and Storage: The extracted butane undergoes purification to remove impurities such as sulfur compounds, water, and other gases. The purified butane is then stored in pressurized tanks or cylinders for distribution.
Key Equipment and Infrastructure
The production of butane requires several pieces of specialized equipment and infrastructure, including:
Gas Processing Units: These units separate butane from other gases in natural gas or crude oil.
Distillation Columns: Used in crude oil refining, distillation columns separate butane from other hydrocarbons based on boiling points.
Compression Systems: These systems are used to compress and store butane in liquefied form, allowing for easier transportation and storage.
Storage Tanks and Cylinders: Butane is stored in large pressurized tanks or cylinders for distribution. These tanks must meet stringent safety standards to handle the flammable nature of butane.
Filtration and Purification Systems: To ensure the quality and purity of the final product, butane undergoes filtration and purification.
Cooling Systems: Butane needs to be cooled during various stages of the production process to ensure its proper condensation and storage.
Control Systems: Advanced control systems monitor temperature, pressure, and flow rates, ensuring safe and efficient production.
Raw Materials and Supply Chain Management
Key raw materials for butane production include:
Natural Gas: A primary source of butane, natural gas must be sourced from reliable suppliers with high-quality reserves.
Crude Oil: For refineries, crude oil serves as the primary feedstock for butane production.
Efficient supply chain management is essential for ensuring the steady availability of raw materials. It involves securing long-term contracts with natural gas and crude oil suppliers, managing transportation logistics, and optimizing inventory management.
Regulatory Compliance and Environmental Considerations
Complying with regulatory standards and addressing environmental concerns is critical for operating a butane manufacturing plant. Key considerations include:
Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA): An EIA should be conducted to assess the plant's impact on the surrounding environment, including air quality, water usage, and waste management.
Safety and Hazardous Material Handling: Butane is highly flammable and requires stringent safety protocols, including proper storage, handling, and emergency response procedures.
Waste Management: The plant must ensure the proper disposal of waste products, including gas emissions, water discharge, and chemical by-products.
Energy Efficiency: Reducing energy consumption and using sustainable energy sources can help minimize the environmental footprint of the plant.
Financial Aspects and Investment Considerations
Establishing a butane manufacturing plant requires significant capital investment. Key financial considerations include:
Capital Investment: The initial costs for land acquisition, plant construction, equipment, and raw materials.
Operating Costs: Ongoing costs include raw materials, energy, labor, and maintenance.
Revenue Generation: Revenue is generated from the sale of butane to various industries, including energy, chemicals, automotive, and pharmaceuticals.
Return on Investment (ROI): The ROI is influenced by factors such as production efficiency, market demand, and operational costs. A well-managed plant can achieve profitability within a few years.
Media Contact
Company Name: Claight Corporation
Contact Person: Peter Fernandas, Corporate Sales Specialist — U.S.A.
Email: sales@expertmarketresearch.com
Toll Free Number: +1–415–325–5166 | +44–702–402–5790
Address: 30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA
Website: www.expertmarketresearch.com
Aus Site: https://www.expertmarketresearch.com.au