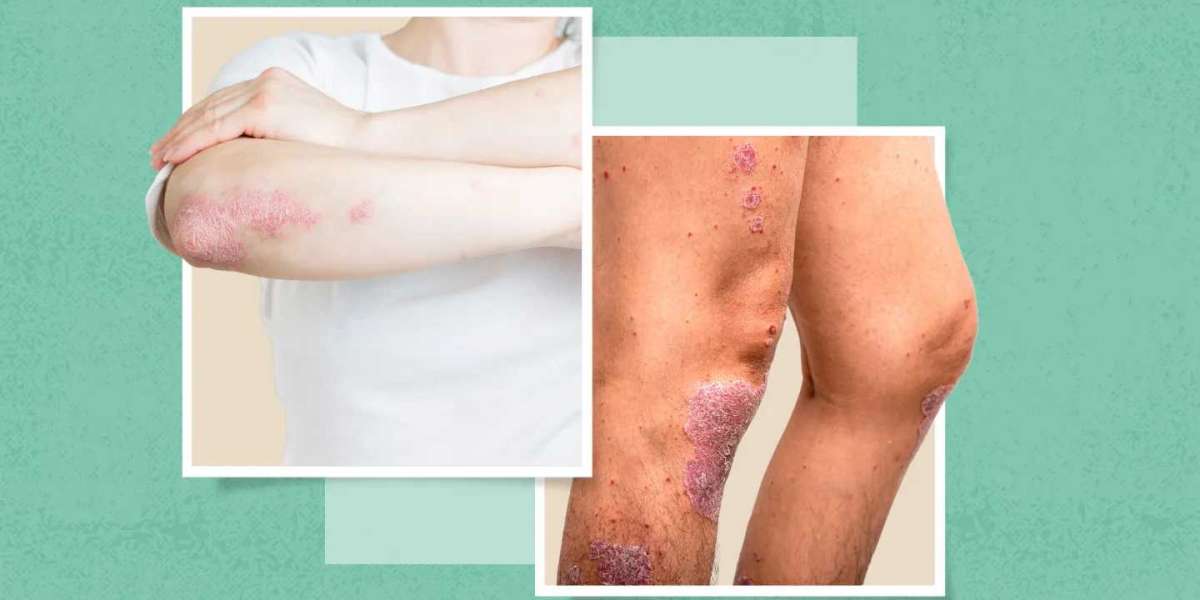
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that affects the skin, causing the rapid growth of skin cells. This results in thick, scaly patches on the skin’s surface. While psoriasis can affect anyone, it often appears during early adulthood or between the ages of 15 and 35. Understanding its causes, symptoms, triggers, and treatment options is essential for managing the condition effectively.
What is Psoriasis?
Psoriasis is a chronic disease that accelerates the skin cell turnover process. Normally, skin cells mature and are shed in about a month. In psoriasis, the process happens in just a few days, causing the cells to accumulate on the skin’s surface, leading to thick, scaly patches. These patches are typically red or inflamed with a silvery-white appearance. Psoriasis is not contagious, meaning it cannot spread from person to person.
Causes of Psoriasis
The exact cause of psoriasis is still unknown, but it is believed to be related to an overactive immune system. The immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, speeding up their growth and causing the skin to become inflamed and scaly. There are two primary factors involved in the development of psoriasis:
- Genetics: A family history of psoriasis increases the likelihood of developing the condition. Specific genes that control the immune system's response to inflammation may play a role in its development.
- Immune System Dysfunction: The immune system of someone with psoriasis reacts abnormally, causing inflammation that leads to the rapid turnover of skin cells.
Common Symptoms of Psoriasis
The symptoms of psoriasis can vary depending on the severity and type of the condition. Some common signs include:
- Red, inflamed patches of skin: These patches are often covered with silvery-white scales.
- Dry, cracked skin: The skin may crack and bleed in severe cases.
- Itching and soreness: Psoriasis can be itchy or painful, especially if the patches are thick or cracked.
- Nail changes: Psoriasis can also affect the nails, causing pitting (small holes) or discoloration.
- Swollen or stiff joints: Some people with psoriasis may also develop psoriatic arthritis, which causes joint inflammation.
While psoriasis may appear on any part of the body, common areas include the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back.
Triggers of Psoriasis
Certain environmental or lifestyle factors can trigger psoriasis flare-ups. Identifying these triggers can help individuals manage their condition better. Some common psoriasis triggers include:
- Stress: High levels of stress can lead to a flare-up or make the condition worse.
- Infections: Strep throat, skin infections, and other illnesses can trigger psoriasis, particularly guttate psoriasis.
- Cold weather: Dry, cold air can irritate the skin and lead to flare-ups.
- Smoking and alcohol: These habits can worsen psoriasis symptoms and even trigger new outbreaks.
- Certain medications: Some medications, like beta-blockers, lithium, and antimalarials, can worsen psoriasis symptoms.
- Injury to the skin: Cuts, scrapes, or even sunburn can trigger new patches of psoriasis in the affected area, known as the Koebner phenomenon.
Effective Treatment Options for Psoriasis
While there is no cure for psoriasis, there are various treatment options available that can help manage symptoms and control flare-ups. The goal is to reduce inflammation, slow down skin cell turnover, and ease discomfort.
- Topical Treatments
Topical treatments are often the first line of defense for psoriasis management. These treatments are applied directly to the skin to reduce inflammation and slow down skin cell turnover.
- Topical Steroids: These are the most commonly prescribed treatments for psoriasis. They work by reducing inflammation and itching. However, they should be used under medical supervision, as prolonged use can cause side effects.
- Vitamin D Analogues: These help slow down skin cell production and can reduce scaling and inflammation.
- Topical Retinoids: Derived from vitamin A, these treatments help normalize skin cell growth and can be particularly useful for those with thick psoriasis plaques.
- Coal Tar: This traditional treatment can help reduce scaling, inflammation, and itching.
- Phototherapy (Light Therapy)
Phototherapy involves exposing the skin to ultraviolet (UV) light under controlled conditions. It can slow the rapid skin cell turnover associated with psoriasis. There are two types of UV therapy:
- UVB Therapy: Uses ultraviolet B light, which is effective in treating moderate to severe psoriasis.
- PUVA Therapy: Combines UVA light with a medication that makes the skin more sensitive to light. This treatment is typically used for more severe cases of psoriasis.
Phototherapy is typically done in a healthcare facility but can also be done at home with the right equipment under the guidance of a dermatologist.
- Systemic Treatments
For severe cases of psoriasis, systemic treatments may be required. These treatments affect the entire body and are generally used when other treatments are not effective.
- Oral Medications: Drugs like methotrexate, cyclosporine, and acitretin can suppress the immune system and help reduce the severity of psoriasis.
- Biologic Drugs: Biologic medications target specific parts of the immune system that are responsible for psoriasis flare-ups. These are usually injected and are typically used for moderate to severe cases.
- Lifestyle Changes and Home Remedies
Managing psoriasis goes beyond medical treatments. Lifestyle changes and home remedies can help manage symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
- Moisturize Regularly: Keeping the skin hydrated is essential for people with psoriasis. Using thick, emollient creams or ointments can reduce dryness and itching.
- Stress Management: Practices such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing can help reduce stress, which is a common trigger for psoriasis.
- Dietary Adjustments: Although there is no specific psoriasis diet, eating anti-inflammatory foods such as fruits, vegetables, and omega-3-rich fish may help manage symptoms.
Book an Appointment with the Best Dermatologist in Karachi through InstaCare
For effective psoriasis treatment, it’s crucial to consult with a qualified dermatologist. In Karachi, you can easily book an appointment with the best dermatologists through InstaCare. They provide a user-friendly platform for booking consultations with top dermatologists, ensuring you receive personalized treatment for your psoriasis.
Conclusion
Psoriasis is a challenging condition that requires ongoing management. While there is no cure, effective treatments and lifestyle adjustments can help reduce symptoms and improve quality of life. By understanding the causes, recognizing triggers, and utilizing a combination of treatments, people with psoriasis can keep flare-ups under control. Always consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best course of treatment for your unique situation.
FAQs
- Can psoriasis be cured?
No, psoriasis is a chronic condition, but it can be managed with the right treatments. The goal is to control symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
- How do I know which psoriasis treatment is right for me?
The best treatment for psoriasis depends on the severity of your condition. A dermatologist can assess your situation and recommend the most suitable treatment options.
- Is psoriasis contagious? No, psoriasis is not contagious. It is an autoimmune condition, so it cannot be spread from person to person through contact.